Refrigerator Defrost Timers are essential components in modern refrigeration systems. They play a crucial role in maintaining optimal performance. By effectively managing ice buildup, these timers ensure the refrigerator operates efficiently. Industry reports indicate that improper defrost cycles can lead to up to 25% energy waste. This highlights the importance of a well-functioning Refrigerator Defrost Timer.
Moreover, the average household could potentially save around $100 annually on energy costs with a reliable timer in place. Many users are unaware of this technology's significance. A malfunctioning defrost timer may cause frost accumulation. This can lead to inconsistent temperatures and spoilage of food items. Understanding the function of the Refrigerator Defrost Timer is vital for both energy conservation and food safety.
However, many consumers overlook this simple device. Regular maintenance is often neglected, resulting in a need for reflection on appliance upkeep. Increased awareness about these mechanisms could ultimately enhance efficiency and extend the lifespan of refrigerators. Investing in technology that maximizes performance is not just smart, but necessary.
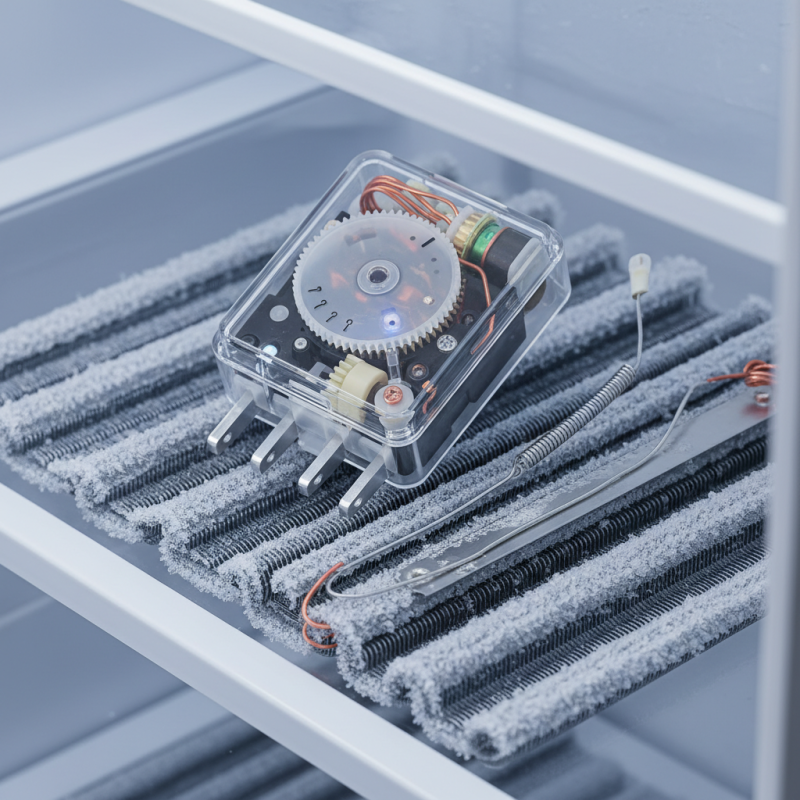

A refrigerator defrost timer plays a crucial role in managing frost buildup. It automates the defrost process, preventing ice from accumulating in your fridge. Without it, frost can block air circulation and hinder the appliance’s efficiency. The timer runs on a set schedule, activating the defrost heater for a specific period. This process melts any ice, draining the water away and maintaining optimal temperature levels.
Understanding its purpose is vital for maintaining your refrigerator. If the timer fails, you may notice frost forming on the coils. This can lead to increased energy consumption. An overloaded fridge also affects cooling. Keep an eye on the frost buildup to spot potential issues early.
**Tips:** Regularly inspect your refrigerator for frost. If you find significant buildup, it may signal a problem with the timer. Also, try setting the temperature correctly. Sometimes, too low a setting leads to excess frost. Be mindful of the door seals too, as drafts can increase ice formation.
| Feature | Description | Functionality | Typical Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | To prevent frost buildup | Cycles through defrost and cooling stages | Every 6-12 hours |
| Types | Mechanical and digital | Controls defrost heater based on timing or temperature | Varies by model |
| Common Issues | Malfunction leading to frost accumulation | Increased energy consumption | Irregular cycles |
| Indicators of Failure | Not defrosting, excessive frost | Wrong temperature readings | Constantly running |

A refrigerator defrost timer is a critical component in frost-free models. It regulates the defrost cycle. When ice builds up, the timer activates the heating element to melt it. This process ensures optimal cooling performance and energy efficiency.
The mechanism is quite straightforward. The timer typically has a cycle duration ranging from eight to twelve hours. Once the timer reaches a specific point, it sends power to the heating element. The defrost heater then warms the evaporator coil. As ice melts, water drains out through a designated pathway. Sometimes, the timer can malfunction, leading to excessive ice formation. This could cause the refrigerator to work harder, affecting its lifespan.
Regular checks on the defrost timer are essential. Users might notice some ice accumulation, indicating potential issues. If the cycle fails, it can lead to significant operational problems. Keeping the timer in good condition can prevent these hassles. It’s a small detail, but it plays an important role in the efficiency of your fridge. Remember, neglecting such aspects can lead to costly repairs down the line.
Defrost timers play a vital role in refrigeration systems. These devices help regulate the defrost cycle. This prevents ice buildup on evaporator coils. Ice accumulation can hinder efficiency and increase energy consumption. According to industry reports, improper defrosting can raise energy usage by up to 30%.
Common types of defrost timers include mechanical, electronic, and adaptive models. Mechanical timers use simple gears and switches. They are cost-effective, but accuracy may vary. Electronic timers offer precise control and programming flexibility. Adaptive timers can learn from usage patterns, optimizing defrost cycles based on actual needs. This technology reduces waste and improves efficiency.
Tips: Regular maintenance is essential. Check the defrost timer settings periodically. An incorrectly set timer can cause unwanted issues. Also, monitoring the frost levels in your refrigerator helps identify potential problems early. Keep the appliance clean for optimal performance. A clean fridge with well-functioning parts reduces the likelihood of breakdowns.
The defrost timer plays a crucial role in a refrigerator's energy efficiency. It regulates how often the refrigerator enters a defrost cycle. Improper settings can lead to excessive energy consumption. For example, a study by the U.S. Department of Energy suggests that a poorly adjusted defrost timer can increase energy use by 15% to 30%. This loss can be significant over time, affecting overall energy bills.
In practice, many users overlook the importance of these settings. They often assume the refrigerator will manage its defrost cycles itself. However, when set too frequently, the unit will expend more energy to compensate for lost cooling. This not only affects energy consumption but can create unnecessary wear and tear on components. The balance between frost buildup and efficiency is delicate. Keeping the defrost timer settings optimized can lead to long-term savings, yet many people remain unaware.
Moreover, energy efficiency is not simply a matter of configuration. The physical condition of the refrigerator matters too. Poor insulation or old components can exacerbate energy waste. Regular maintenance, including checking seals and cleaning coils, is essential. A defrost timer works best when the entire system operates correctly. Understanding this interconnectedness can lead to smarter choices and reduced energy usage.
Refrigerator defrost timers play a vital role in keeping your appliance running smoothly. They help manage the defrost cycle, preventing ice buildup. However, issues can arise, leading to malfunctioning timers. For instance, if frost accumulates inside, the timer might not be functioning properly. It could be stuck or damaged. A visual inspection can help. Check for any blockages or signs of wear.
Another common issue is the timer not advancing. This can lead to continuous ice formation. Listen for any clicking or buzzing sounds. These sounds can indicate problems within the timer mechanism. In some cases, the timer might need resetting. Unplugging the refrigerator for a short period can sometimes resolve this issue. However, don’t rush into repairs. Always consider consulting a professional if the problem persists.
Poor installation can also cause timer issues. If the timer is improperly aligned, it might not work as intended. Keep track of any changes in performance. A decrease in cooling efficiency might signal that the timer is the culprit. Regular maintenance checks can help detect such problems early.
This bar chart illustrates the average defrost time for refrigerators throughout the months of the year. Variations in defrost time can occur due to external temperatures, usage frequency, and the efficiency of the defrost timer mechanism.